The post Absorption Costing | Variable Costing | Exam Based Q&A | Brief | Descriptive | Analytical appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>
Absorption Costing and Variable Costing Exam Based Questions and Answers
It includes Brief Question, Descriptive Questions and Analytical Questions with answers in details
Absorption Costing | External Costing | Traditional Costing
Absorption costing is a traditional costing system.
It is also called full absorption, conventional costing or traditional costing and external costing.
It includes variable cost and fixed cost manufacturing.
Absorption costing includes direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost and fixed manufacturing cost in product cost.
It includes administrative cost, selling and distribution cost in period cost.
But it does not include fixed manufacturing cost in period cost.
The main object of the business company is to earn more and more profit.
Success or failure of the company is depended on profit.
The income statement measures profit or loss of the company.
There are two types of methods to find out profit and loss from income statement.
Absorption costing and variable costing are two methods to prepare income statement.
Absorption costing is suitable for internal as well as external users but variable costing is suitable for internal users with management decision.
Direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost and fixed manufacturing cost = Production units × Cost per unit
Period cost under absorption costing = Administrative cost + Selling and distribution cost
Total variable, selling and distribution cost = Sales units × Cost per unit
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For ….. units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
||
|
Sales Revenue (sales units @ $) |
xxxx |
||
|
(A) |
xxxx |
||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
||
|
|
Direct materials (production units @ $) |
|
|
|
|
Direct labour (production units @ $) |
|
|
|
|
Variable production overhead (production units @ $) |
|
|
|
|
Fixed production cost (production units @ $*) |
|
|
|
|
Total manufacturing cost or Cost of production |
xxxx |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory (opening stock @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory (closing stock @ $) |
(xxx) |
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
xxxx |
|
|
Add: |
Under absorption# manufacturing cost (compare with actual) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Over absorption manufacturing cost (compare with actual) |
(xxx) |
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost (production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Variable S&D cost (sales units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed administrative cost (production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Fixed S & D cost (sales units x $) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Net Income |
$xxxx |
||
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU*) = Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
Either over absorption# or under absorption
Variable Costing | Internal Costing | Direct Costing
Variable costing is also known as internal costing, direct costing and marginal costing.
Variable cost helps to administrator to solve the problem about production planning.
Under this method, production cost is calculated on variable basis.
Variable costing includes direct materials, direct labour and variable manufacturing cost in product cost.
It includes fixed manufacturing cost, administrative, selling and distribution cost in period cost.
Direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost:
= Production units x Cost per unit
Period costing under variable costing = Fixed manufacturing cost + Administrative cost + S&D cost
Total variable, selling and distribution cost = Sales units × Cost per unit
Sold units = Opening stock + Production – Closing stock
Income Statement under Variable Costing
|
Particulars |
Amount $ |
|||
|
Sales revenue (sales units @ $) |
xxxx |
|||
|
(A) |
xxxx |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|||
|
|
Direct materials |
(production units @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
(production units @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Variable production overhead |
(production units @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Total variable cost or Cost of production |
xxxx |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
(opening stock @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
(closing stock @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
(production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
(sales units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Net contribution |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
( ± absorption, if any) |
xxxx |
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
(production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
(sales units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Net Income |
$xxxx |
|||
Note: If there is under absorption in absorption costing, it is added with fixed manufacturing cost in variable costing
If there is over absorption in absorption costing, it is deducted from fixed manufacturing cost in variable costing
Reconciliation of Difference in Net Cost
If there is no difference in the size of opening stock and closing stock, in such a condition net income of absorption costing and variance costing is same.
The difference between opening stock, closing stock and fixed manufacturing overhead are the main cause of difference in net income.
These differences can be solved by reconciliation.
Where:
|
Difference in stock units |
= Difference in income ÷ Fixed cost per unit |
|
According to variable costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units − Difference in stock units |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units + Difference in stock units |
|
|
|
|
According to variable costing, Closing stock– Opening stock |
= Difference |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock – Closing stock |
= Difference |
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
Click on the photo for FREE eBooks
Brief Questions
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 1
The extracted data are given to you:
Opening stock 10,000 units
Sales 60,000 units
Closing stock 20,000 units
Required: Production units
[Answer: 70,000 units]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 2
The extracted data are given to you:
Production 20,000 units
Sales 25,000 units
Required: Stock
[Answer: Opening stock = 5,000 units]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 3
The extracted data are taken from ABC Manufactures Company:
Sales units 9,000 units
Production units 12,000 units
Cost data:
Direct materials 60
Direct labor 40
Variable factory overheads 30
Fixed manufacturing overheads $180,000
Required: Cost of production under variable costing
[Answer: COP = $15,60,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 4
The extracted data are taken from BC Manufactures Company:
Production units 12,000 units
Normal output 9,000 units
Cost data:
Direct materials 60
Direct labor 40
Variable factory overheads 30
Fixed manufacturing overheads $180,000
Required: Cost of production under absorption costing
[Answer: COP = $18,00,000] * FCPU or SFOR = $20
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 5
ABC Manufacturing Company has following extracted data:
Normal output 35,000 units
Production 30,000 units
Opening stock 5,000 units
Closing stock 10,000 units
Cost data per unit:
Direct materials $260,000
Direct labour $350,000
Variable factory overheads $275,000
Factory manufacturing overheads $200,000
Required: Cost of goods sold under variable costing
[Answer: COGS = $735,500]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 6
ABC Manufacturing Company has following extracted data:
Standard fixed overhead rate (SFOR) $7
Production 30,000 units
Sales 35,000 units
Opening stock 10,000 units
Cost data per unit:
Direct materials $260,000
Direct labour $350,000
Variable factory overheads $275,000
Required: Cost of goods sold under absorption costing
[Answer: COGS = $12,77,500] *Closing stock = 5,000 units
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 7
The following extracted information is available:
Net income as per absorption costing $450,000
Opening stock 10,000 units
Closing stock 20,000 units
Normal output was 40,000 units
Fixed manufacturing cost $200,000
Required: Reconciliation statement
[Answer: Net profit as per variable costing = $400,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 8
The following extracted information is available:
Net income as per variable costing $450,000
Opening stock 10,000 units
Closing stock 20,000 units
Normal output was 40,000 units
Fixed manufacturing cost $200,000
Required: Reconciliation statement
[Answer: Net profit as per absorption costing = $500,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 9
Following extracted information is given to you:
Cost of goods sold before adjustment $500,000
Fixed manufacturing cost $125,000
Normal output 25,000 units
Output for the period 30,000 units
Required: Cost of goods sold after adjustment
[Answer: $475,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
BQ: 10
Following extracted information is given to you:
Cost of goods sold before adjustment $500,000
Fixed manufacturing cost $125,000
Normal output 25,000 units
Output for the period 22,000 units
Required: Cost of goods sold after adjustment
[Answer: $515,000]
######
|
Click on the link for YouTube videos |
|
|
Accounting Equation |
|
|
Journal Entries in Nepali |
|
|
Journal Entries |
|
|
Journal Entry and Ledger |
|
|
Ledger |
|
|
Subsidiary Book |
|
|
Cashbook |
|
|
Trial Balance and Adjusted Trial Balance |
|
|
Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) |
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
Click on the link for YouTube videos chapter wise |
|
|
Financial Accounting and Analysis (All videos) |
|
|
Accounting Process |
|
|
Accounting for Long Lived Assets |
|
|
Analysis of Financial Statement |
|
######
Descriptive Questions
VARIABLE COSTING
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 1
Following are data pertaining to month of December of operation for ABC Textile Company related to school dress:
|
Opening stock 2,000 units |
Administrative expenses: |
|
Units produced 6,000 units |
Fixed $250,000 |
|
Normal output 5,000 units |
Variable $250,000 |
|
Units sold 7,000 units |
|
|
Selling price per unit $300 |
Selling and distribution expenses: |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost $200,000 |
Variable (per unit) $20 |
|
Variable cost per unit: |
Fixed (per unit) $15 |
|
Direct materials 50 |
|
|
Direct labor 40 |
|
|
Factory overheads 30 |
|
Required: (a) Income statement under variable costing; (b) Reconciliation statement
[Answer :(1) Net income = $315,000; (2) $275,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 2
AK Manufacturing Company has reported its income statement under absorption costing technique as under:
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue (10,000 units x $45) |
|
450,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Cost of goods sold: |
|
|
|
|
Beginning inventory (2,000 x $27) |
54,000 |
|
|
|
Variable cost (9,000 x $23) |
207,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed mfg. cost (9,000 x $4) |
36,000 |
|
|
|
Ending inventory (1,000 x $27) |
(27,000) |
(270,000) |
|
|
Gross margin before adjustment |
|
180,000 |
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost under absorbed |
|
4,000 |
|
|
Gross margin after adjustment |
|
176,000 |
|
Less: |
Other variable cost |
|
50,000 |
|
Net income before tax |
|
$126,000 |
|
Required: Income statement under variable costing technique
[Answer: Net income under variable costing = $130,000;
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 3
Following extracted details are given to you by EP Industries:
Normal capacity 200,000 units per year
Standard variable manufacturing expenses $20 per unit
Fixed manufacturing overhead $300,000 per year
Variable selling expenses $2 per unit
Fixed selling expenses $100,000
Unit sale price $25
The operating results for the year ending December of the last year were as follows
Sales 150,000 units
Production 180,000 units
Required: (a) variable costing income statement; (b) Reconciled profit under absorption costing
[Answers: Income under VC = $50,000, under AC = $95,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 4
XYZ Manufacturing Company with normal capacity of 50,000 units supplied you with the following particular:
|
Production |
55,000 units |
|
Sale |
60,000 units |
|
Closing stock |
5,000 units |
|
Unit variable manufacturing cost |
$6 |
|
Unit fixed manufacturing overhead |
$3 |
|
Unit variable selling and administrative cost |
$2 |
|
Fixed selling & administrative cost |
$90,000 |
|
Unit selling price |
$15 |
Required: (1) Variable costing income statement; (2) Reconciled profit under absorption costing
[Answers: (1) $180,000; (2) $165,000]
ABSORPTION COSTING
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 5
The extracted cost abstract of EP Manufacturing Company was as follows:
|
Particulars |
Units cost |
The operations of the year ended December 2021 were: |
|
|
Direct materials |
$12 |
Opening stock |
10,000 units |
|
Direct labour |
$3 |
Production |
90,000 units |
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
$2 |
Sales |
80,000 units |
|
Variable selling & distribution expenses |
$1 |
Sales price per unit |
$30 |
Budgeted normal output was 100,000 units with $200,000 fixed manufacturing cost. The fixed selling and distribution expenses were $50,000
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answer: Net profit: A.C = $730,000; V.C = $710,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 6
The summarized data of AM Manufacturing Concern for a capacity output of 50,000 units for a year is reported as:
|
Items |
Units Cost |
Items |
Units Cost |
|
Direct materials |
$14 |
Fixed manufacturing overhead |
$75,000 annual |
|
Direct labour |
$6 |
Fixed selling expenses |
$50,000 annual |
|
Variable manufacturing overhead |
$4 |
Production |
45,000 units |
|
Variable selling expenses |
$2 |
Sales |
40,000 units |
|
Sales price per unit |
$30 |
|
|
Required: (1) Absorption costing income statement; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answers: (1) Net income = $42,500; (2) $35,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 7
ABC Manufacturing Company with normal capacity of 20,000 units furnished you the following information:
|
Beginning inventory units |
3,000 |
Standard variable cost |
$6.50 |
|
Units produced during the year |
18,000 |
Fixed factory overhead at normal capacity |
$50,000 |
|
Units sold during the year |
20,000 |
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
$5,000 |
|
|
|
Unit selling price |
$12 |
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answers: (1) $50,000; (2) $55,000] *Under absorption = $5,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 8
Following are the references data of month June of operation for XYZ Company:
|
Opening stock |
15,000 units |
Variable cost: |
|
|
Units produced |
45,000 units |
Direct materials per unit |
$4 |
|
Units sold |
50,000 units |
Direct labour per unit |
$2 |
|
Normal output |
50,000 units |
Factory overheads per unit |
$1 |
|
Selling price per unit |
$20 |
Administrative |
$50,000 |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
$150,000 |
Selling and distribution per unit |
$1 |
|
|
|
Fixed cost: |
|
|
|
|
Manufacturing |
$150,000 |
|
|
|
Administrative |
$40,000 |
|
|
|
Selling and distribution |
$30,000 |
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: (1) Net income = $315,000; (2) $330,000]
ABSORPTION AND VARIABLE COSTING
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
DQ: 9
Max Company uses direct costing for internal control purchase and absorption costing for external reporting purpose. The following differences are located while comparing the two statements.
|
Items |
Variable Costing |
Absorption Costing |
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
$60,000 |
$60,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost charged |
$25,000 |
$30,000 |
|
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
$40,000 |
$40,000 |
|
|
Variable selling cost per unit |
$2 |
$2 |
|
|
Selling price per unit |
$30 |
$30 |
|
Management also projected the following data for the inventory:
|
Beginning inventory units 1,000 |
Sales units 5,000 |
|
Production units 6,000 |
Closing stock units 2,000 |
Cost of beginning inventory is the same as the cost of production in the period.
Required: Income statement by using absorption costing and variable costing approach
[Answers: Net profit = $30,000; $25,000]
*Over absorption $5,000]
Click on the photo for FREE eBooks
Analytical Questions
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 1
Fame Readymade Garment has given following data at the end of December 2020; it was anticipated that sales would rise 20% in year 2021. Therefore, production was increased from 20,000 units to meet this expected demand.
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Sales units during year |
20,000 |
|
Selling price per unit |
300 |
|
Direct materials |
45 |
|
Direct labors |
75 |
|
Variable manufacturing overheads |
30 |
|
Variable administrative expenses |
2,50,000 |
|
Variable selling and distribution expenses |
1,00,000 |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost for the year |
9,60,000 |
|
Fixed administrative cost |
6,00,000 |
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
4,00,000 |
All taxes are to be ignored. The beginning inventory of the year was nil.
You are required to prepare profit statement for the year ending December 2021
(1) Net income as per variable costing; (2) Net income as per absorption costing
[Answer: (1) V.C. = $690,000 (2) A.C. = $10,90,000;
* Over absorption = $240,000; Production = 24,000 units]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 2
XYZ Ltd uses direct costing for internal control purposes and absorption costing for external reporting purposes. The company uses the following unit costs for the one product it manufactures:
|
Projected cost per unit: |
|
|
Direct materials |
$60 |
|
Direct labour |
$38 |
|
Variable manufacturing |
$12 |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
$10 (Based on 10,000 units per month) |
|
Variable selling and administrative cost |
$8 |
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
$5.60 (Based on 10,000 units per month) |
The projected selling price is $160 per unit. The fixed costs remain fixed within the relevant range of 4,000 to 16,000 units of production.
Management has also projected the following data for the month:
Opening stock 2,000 units
Production 9,000 units
Sales 7,500 units
Required: projected income statement under direct costing and absorption costing.
[Answer: Variable costing: $1,59,000, Absorption costing: $1,74,000;
* Under absorption cost =100,000 – 90,000 = 10,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 3
ABC Manufacturing Company has following data:
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
[For 14,000 units]
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales |
[16,000 @ $80] [A] |
12,80,000 |
||
|
Manufacturing of goods sold: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[14,000 units @ $20] |
280,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[14,000 units @ $10] |
140,000 |
|
|
|
Variable production cost |
[14,000 units @ $15] |
210,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[14,000 units @ $5] |
70,000 |
|
|
|
|
Manufacturing cost @ $50] |
700,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Opening stock |
[3,000 units @ $50] |
150,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Closing Stock |
[1,000 units @ $50] |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
800,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Under absorption of fixed mfg cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
850,000 |
|
|
|
|
Gross profit [A –B] |
430,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Administrative and selling cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed |
|
80,000 |
|
|
|
Variable |
|
50,000 |
130,000 |
|
Net income |
300,000 |
|||
Required: (a) Income statement under variable costing;
(b) Reconciliation of profit between absorption costing and variable costing.
[Answer: Net income under V.C. = $3,10,000;
* Fixed Manufacturing cost in V.C = $120,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 4
MS Tech (P) Ltd produces and assembles computer components. The following internal data is available:
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 20,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[21,000 units @ $100] |
21,00,000 |
||
|
(A) |
21,00,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[20,000 units @ $30] |
6,00,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[20,000 units @ $15] |
3,00,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[20,000 units @ $10] |
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $55) |
11,00,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[2,000 units @ $55] |
1,10,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending Inventory |
[1,000 units @ $55] |
55,000 |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
11,55,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
9,45,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable selling administrative cost |
|
1,05,000 |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
8,40,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
|
420,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
|
+ 350,000 |
7,70,000 |
|
Net income |
70,000 |
|||
Normal capacity for the period is 20,000 units.
Required: (1) Net income under external period; (2) Reconciliation statement for the period
[Answer: Net income under A.C. = $49,000; * FCPU = $21]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 5
The following information is given by DT Manufacturing Company:
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 27,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[28,000 units @ $30] |
840,000 |
||
|
(A) |
840,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
– |
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[27,000 units @ $5] |
135,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[27,000 units @ $8] |
216,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[27,000 units @ $5] |
135,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $18) |
486,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[3,000 units @ $18] |
54,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending Inventory |
[2,000 units @ $18] |
36,000 |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
504,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
336,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative and selling cost |
|
86,000 |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
250,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
|
100,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
|
+ 50,000 |
150,000 |
|
Net income |
100,000 |
|||
Normal capacity for the period is 25,000 units.
Required: (1) Conversion the income statement into absorption costing statement; (2) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: (1) $96,000; (2) $100,000;
* Over absorption = $8,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 6
The following information is available from Nepal Polymers (P) Ltd:
|
Particulars |
January |
February |
|
Selling price per unit |
$100 |
$100 |
|
Direct materials and labour per unit |
$25 |
$25 |
|
Variable manufacturing cost per unit |
$15 |
$15 |
|
Variable selling and administrative cost per unit |
$10 |
$10 |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
$140,000 |
$140,000 |
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
10% of sales |
10% of sales |
|
Units |
January |
February |
|
Production units |
6,000 |
8,000 |
|
Sales units |
5,500 |
7,000 |
Normal output is 7,000 units per month
Required: (1) Income statement under variable costing; (2) Income statement under absorption costing
[Answer: (1) V.C. = $80,000 and $140,000;
(2) A.C. = $90,000 and $160,000;
* Closing stock in Jan = 500 units; Feb = 1,500 units;
*Under absorption in January = $20,000;
Over absorption in February = $20,000
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
AQ: 7
A manufacturing company provides you the following data for three accounting periods:
Standard capacity is 10,000 units per month. Fixed manufacturing costs budgeted per month $400,000
Production, sales and inventory changes were as follows:
|
Period |
Standard capacity |
Produced units |
Sold units |
|
|
January |
90% |
9,000 |
9,000 |
|
|
February |
110% |
11,000 |
9,000 |
|
|
March |
85% |
8,500 |
10,000 |
|
Standard capacity utilized by 10,000 units
Other information:
|
Administrative and selling expenses were: |
Variable cost per unit was as following: |
|
Variable $20 per unit |
Materials $40 |
|
Fixed selling price per period $300,000 |
Direct labour $40 |
|
|
Manufacturing $20 |
|
|
Selling price per unit $200 |
Determine the income under:
(1) Absorption costing for three months; (2) Marginal costing for three months
(3) Reconciliation of the difference between the net incomes reported under two concepts.
[Answer: (1) $20,000, $100,000, $40,000 (2) $20,000, $20,000, $100,000]
* Absorption: Under in January = $40,000; Over in February = $40,000;
Under in March = $60,000]
EP Online Study
Thank you for investing your time.
Please comment on the article.
You can help us by sharing this post on your social media platform.
Jay Google, Jay YouTube, Jay Social Media
जय गूगल. जय युट्युब, जय सोशल मीडिया
The post Absorption Costing | Variable Costing | Exam Based Q&A | Brief | Descriptive | Analytical appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>The post Absorption costing | Variable costing | Reconciliation Statement | Problems and solutions appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>
Absorption Costing | External Costing | Traditional Costing
Absorption costing is a traditional costing system.
It is also called full absorption, conventional costing or traditional costing and external costing.
It includes variable cost and fixed cost manufacturing.
Absorption costing includes direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost and fixed manufacturing cost in product cost.
It includes administrative cost, selling and distribution cost in period cost.
But it does not include fixed manufacturing cost in period cost.
The main object of the business company is to earn more and more profit.
Success or failure of the company is depended on profit.
The income statement measures profit or loss of the company.
There are two types of methods to find out profit and loss from income statement.
Absorption costing and variable costing are two methods to prepare income statement.
Absorption costing is suitable for internal as well as external users but variable costing is suitable for internal users with management decision.
Direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost and fixed manufacturing cost = Production units × Cost per unit
Period cost under absorption costing = Administrative cost + Selling and distribution cost
Total variable, selling and distribution cost = Sales units × Cost per unit
Variable Costing | Internal Costing | Direct Costing
Variable costing is also known as internal costing, direct costing and marginal costing.
Variable cost helps to administrator to solve the problem about production planning.
Under this method, production cost is calculated on variable basis.
Variable costing includes direct materials, direct labour and variable manufacturing cost in product cost.
It includes fixed manufacturing cost, administrative, selling and distribution cost in period cost.
Direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost:
= Production units x Cost per unit
Period costing under variable costing = Fixed manufacturing cost + Administrative cost + S&D cost
Total variable, selling and distribution cost = Sales units × Cost per unit
Sold units = Opening stock + Production – Closing stock
Reconciliation of Difference in Net Cost
If there is no difference in the size of opening stock and closing stock, in such a condition net income of absorption costing and variance costing is same.
The difference between opening stock, closing stock and fixed manufacturing overhead are the main cause of difference in net income.
These differences can be solved by reconciliation.
Where:
|
Difference in stock units |
= Difference in income ÷ Fixed cost per unit |
|
According to variable costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units − Difference in stock units |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units + Difference in stock units |
|
|
|
|
According to variable costing, Closing stock– Opening stock |
= Difference |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock – Closing stock |
= Difference |
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Different in income |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Opening stock in units |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Closing stock in units |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Different stock in units (A) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Fixed cost per unit (B) |
x |
x |
|
Different in income (A x B) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
FMC = fixed manufacturing cost per unit |
|
|
FCPU = fixed cost per unit |
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output |
|
SFOR = standard fixed overhead rate |
|
######
|
Click on the link for YouTube videos |
|
|
Accounting Equation |
|
|
Journal Entries in Nepali |
|
|
Journal Entries |
|
|
Journal Entry and Ledger |
|
|
Ledger |
|
|
Subsidiary Book |
|
|
Cashbook |
|
|
Trial Balance and Adjusted Trial Balance |
|
|
Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) |
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
Click on the link for YouTube videos chapter wise |
|
|
Financial Accounting and Analysis (All videos) |
|
|
Accounting Process |
|
|
Accounting for Long Lived Assets |
|
|
Analysis of Financial Statement |
|
######
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3A
Nepal Beverages Limited produces mineral water. It sales its product in 10 liter’s pet jar.
The normal annual level of operations is 36,000 units. Data for the last financial years 2020 was as follows:
|
Production |
40,000 units |
|
Sales |
32,000 units |
|
Selling price per units |
$60 |
|
Costs per units: |
|
|
Direct materials |
$14 |
|
Direct labors |
$12 |
|
Variable manufacturing overheads |
$8 |
|
Fixed manufacturing overheads |
$2,16,000 (based on normal output) |
|
Administrative costs: |
|
|
Fixed |
$50,000 |
|
Variable |
5% of sales revenue |
|
Selling and distribution overhead: |
|
|
Fixed |
$30,000 |
|
Variable |
5% of selling price per unit |
There was no opening stock of finished goods and the work-in-progress.
You are required to: (i) Prepare an income statement based on direct costing for the year ended 2021
(ii) Prepare an income statement based on absorption costing for the year ended 2021
(iii) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: (i) $320,000 (ii) $368,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
32,000 |
= |
Nil + 40,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
8,000 units |
|
Again, |
|
|
|
Fixed cost per unit [FCPU] |
= |
Factory overhead ÷ Normal output |
|
|
= |
$216,000 ÷ 36,000 units |
|
|
= |
$6 |
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 40,000 cases
|
Particulars |
|
Amount |
||
|
Sales revenue |
[32,000 units @ $60] |
19,20,000 |
||
|
(A) |
19,20,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[40,000 units @ $12] |
4,80,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[40,000 units @ $14] |
5,60,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[40,000 units @ $8] |
3,20,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $34) |
13,60,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[0 units @ $34] |
– |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[8,000 units @ $34] |
2,72,000 |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
10,88,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
8,32,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
[sales @5% = 19,20,000@5%] |
(96,000) |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
[40,000 x 60@5%] |
(1,20,000) |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
6,16,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[given] |
216,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
[given] |
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
[given] |
30,000 |
(2,96,000) |
|
Net Income |
$3,20,000 |
|||
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 40,000 cases
|
Particulars |
|
Amount |
||
|
Sales revenue |
[32,000 units @ $60] |
19,20,000 |
||
|
(A) |
19,20,000 |
|||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[40,000 units @ $12] |
4,80,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[40,000 units @ $14] |
5,60,000 |
|
|
|
Variable production cost |
[40,000 units @ $8] |
3,20,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[40,000 units @ $6] |
2,40,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ 40) |
16,00,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[0 units @ $40] |
Nil |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[8,000 units @ $40] |
3,20,000 |
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
12,80,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Under absorption |
|
– |
|
|
Less: |
Over absorption |
[$240,000 A.C. – $216,000 V.C.] |
24,000 |
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
12,56,000 |
||
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
6,64,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
96,000 |
|
|
|
Variable S&D cost |
|
120,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed administrative cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
|
30,000 |
(2,96,000) |
|
Net Income |
$3,68,000 |
|||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable cost |
320,000 |
|
Add: Closing stock (8,000 units @ $6) |
48,000 |
|
Less: Opening stock (0 units @ $6) |
Nil |
|
Net income as per absorption cost |
$368,000 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3B
ABC Manufacturing Company has following information related to a product:
|
Year |
Production |
Sales |
Sales price per unit |
|
2019 |
170,000 |
140,000 |
$25 |
|
2020 |
140,000 |
160,000 |
$25 |
Other information:
|
Normal production 150,000 units |
Variable cost per unit: |
Administrative and selling cost: |
|
Fixed production cost $750,000 |
Direct materials $5 |
Variable 5% of sales |
|
|
Direct labour $6 |
Fixed $325,000 |
|
|
Production cost $4 |
|
Required: (1) Income statement under variable costing for 2020 and 2021
(2) Income statement under absorption costing for 2020 and 2021;
(3) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: Variable costing 150,000 and 325,000;
Absorption costing 300,000 and 225,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
140,000 |
= |
Nil + 170,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
30,000 |
Closing stock of last year becomes opening stock of current year
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
140,000 |
= |
30,000 + 140,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
10,000 |
Fixed cost per unit [FCPU]
= Factory overhead old ÷ Normal output
= $750,000 ÷ 150,000 units
= $5
Income Statement under Variable Costing
170,000 and 140,000 units
|
Particulars |
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
||
|
Sales revenue |
[sold units @ $25] |
35,00,000 |
40,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
35,00,000 |
40,00,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
– |
|
|
|
|
Direct materials |
[production @ $5] |
8,50,000 |
7,00,000 |
|
|
Direct labour |
[production @ $6] |
10,20,000 |
8,40,000 |
|
|
Variable production cost |
[production @ $4] |
6,80,000 |
5,60,000 |
|
|
Cost of production (amount ÷ units = $15) |
25,50,000 |
24,00,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[units @ $15] |
– |
4,50,000 |
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[units @ $15] |
(450,000) |
(150,000) |
|
|
COGS (B) |
21,00,000 |
24,00,000 |
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
14,00,000 |
16,00,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable selling and admt cost |
[sales@5%] |
(175,000) |
(200,000) |
|
|
Net contribution |
12,25,000 |
14,00,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
|
(750,000) |
(750,000) |
|
|
Fixed selling and admt cost |
|
(325,000) |
(325,000) |
|
Net Income |
$1,50,000 |
$3,25,000 |
||
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
170,000 and 140,000 units
|
Particulars |
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
||
|
Sales revenue |
[sold units @ $25] |
35,00,000 |
40,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
35,00,000 |
40,00,000 |
||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
– |
|
|
|
|
Direct materials |
[production @ $5] |
8,50,000 |
7,00,000 |
|
|
Direct labour |
[production @ $6] |
10,20,000 |
8,40,000 |
|
|
Variable production cost |
[production @ $4] |
6,80,000 |
5,60,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost |
[production @ $5] |
8,50,000 |
7,00,000 |
|
|
Cost of production (amount ÷ units = $20) |
34,00,000 |
28,00,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[units @ $20] |
– |
6,00,000 |
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[units @ $20] |
(600,000) |
(200,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
28,00,000 |
32,00,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Under absorption |
[compare with variable costing] |
– |
50,000 |
|
Less: |
Over absorption |
[compare with variable costing] |
1,00,000 |
– |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
27,00,000 |
32,50,000 |
|
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
8,00,000 |
7,50,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable selling and admt cost |
[sales@5%] |
(175,000) |
(200,000) |
|
Less: |
Fixed selling and admt cost |
|
(325,000) |
(325,000) |
|
Net Income |
$3,00,000 |
$2,25,000 |
||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
|||
|
Net income as per variable costing |
150,000 |
325,000 |
|||
|
Add: Closing stock |
30,000 |
10,000 |
@ $5 |
150,000 |
50,000 |
|
Less: Opening stock |
Nil |
30,000 |
@ $5 |
Nil |
(150,000) |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
$300,000 |
$225,000 |
|||
Closing stock of year 1 becomes opening stock of year 2, here $30,000
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3C
ABC Manufacturing Company has following information related to a product:
|
Year |
Production |
Sales |
Sales price per unit |
|
2019 |
6,000 |
4,000 |
$300 |
|
2020 |
4,000 |
5,000 |
$300 |
|
2021 |
5,000 |
6,000 |
$300 |
Other information:
|
Normal production 5,000 units |
Variable cost per unit: |
Administrative and selling cost: |
|
|
Fixed production cost $500,000 |
Direct materials |
$60 |
Variable 5% of sales |
|
|
Direct labour |
$30 |
Fixed $100,000 |
|
|
Variable production cost |
$10 |
|
|
|
Total |
$100 |
|
Required: (1) Income statement under variable costing for 2019, 2020 and 2021
(2) Income statement under absorption costing for 2019, 2020 and 2021
(3) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: Variable costing: 2019= $140,000; 2020 = $325,000; 2021 = $510,000;
Absorption costing: 2019 = $340,000; 2020 = $225,000; 2021 = $410,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
Year 2019
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
4,000 |
= |
Nil + 6,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
2,000 |
Closing stock of last year becomes opening stock of current year
Year 2020
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
5,000 |
= |
2,000 + 4000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
1,000 |
Year 2021
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
6,000 |
= |
1,000 + 5000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
Nil |
Fixed cost per unit [FCPU]
= Factory overhead old ÷ Normal output
= $500,000 ÷ 50,000 units
= $100
Income Statement under Variable Costing
6,000; 4,000 and 5,000 units
|
Particulars |
Year 2019 |
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
||
|
Sales revenue |
[sold units @ $200] |
12,00,000 |
15,00,000 |
18,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
12,00,000 |
15,00,000 |
18,00,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials |
[production @ $60] |
3,60,000 |
2,40,000 |
3,00,000 |
|
|
Direct labour |
[production @ $30] |
1,80,000 |
1,20,000 |
1,50,000 |
|
|
Variable production cost |
[production @ $10] |
60,000 |
40,000 |
50,000 |
|
|
Cost of production ($ ÷ units = $100) |
$6,00,000 |
$4,00,000 |
$5,00,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[units @ $100] |
– |
2,00,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[units @ $100] |
(200,000) |
(100,000) |
Nil |
|
|
COGS (B) |
4,00,000 |
500,000 |
6,00,000 |
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
800,000 |
10,00,000 |
12,00,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable selling and admt cost |
[sales@5%] |
(60,000) |
(75,000) |
(90,000) |
|
|
Net contribution |
7,40,000 |
9,25,000 |
11,10,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
|
(500,000) |
(500,000) |
(5,00,000) |
|
|
Fixed selling and admt cost |
|
(100,000) |
(100,000) |
(100,000) |
|
Net Income |
1,40,000 |
3,25,000 |
5,10,000 |
||
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
6,000; 4,000 and 5,000 units
|
Particulars |
Year 2019 |
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
||
|
Sales revenue |
[sold units @ $25] |
12,00,000 |
15,00,000 |
18,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
12,00,000 |
15,00,000 |
18,00,000 |
||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials |
[production @ $60] |
3,60,000 |
2,40,000 |
3,00,000 |
|
|
Direct labour |
[production @ $30] |
1,80,000 |
1,20,000 |
1,50,000 |
|
|
Variable production cost |
[production @ $10] |
60,000 |
40,000 |
50,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost |
[production @ $100] |
6,00,000 |
4,00,000 |
5,00,000 |
|
|
Cost of production (amount ÷ units = $200) |
12,00,000 |
8,00,000 |
10,00,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[units @ $200] |
– |
4,00,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[units @ $200] |
(400,000) |
(200,000) |
– |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
8,00,000 |
10,00,000 |
12,00,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Under absorption |
[compare with variable costing] |
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Over absorption |
[compare with variable costing] |
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
7,00,000 |
11,00,000 |
12,00,000 |
|
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
5,00,000 |
4,00,000 |
6,00,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable admt and selling cost |
[sales@5%] |
(60,000) |
(75,000) |
(90,000) |
|
Less: |
Fixed admt and selling cost |
|
(100,000) |
(100,000) |
(100,000) |
|
Net Income |
3,40,000 |
2,25,000 |
4,10,000 |
||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Year 2019 |
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
||||
|
Net income as per variable costing |
1,40,000 |
3,25,000 |
5,10,000 |
||||
|
Add: Closing stock |
2,000 |
1,000 |
Nil |
@ $100 |
2,00,000 |
1,00,000 |
Nil |
|
Less: Opening stock |
Nil |
2,000 |
1,000 |
@ $100 |
Nil |
(200,000) |
(100,000) |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
3,40,000 |
2,25,000 |
4,10,000 |
||||
Closing stock of year 1 becomes opening stock of year 2, here $2,000 and 1,000
WHEN QUESTION IS GIVEN IN VARIABLE OR ABSORPTION COSTING
Sometime variable costing or absorption costing is given in the question.
In such a condition, you can be asked to calculate:
When question is given in variable costing you are asked to calculate absorption costing and reconciliation statement.
When question is given in absorption costing you are asked to calculate variable costing and reconciliation statement.
The Relationships between Production, Sales and Profit
|
Conditions |
Result |
Reason |
|
Sales = Production |
Profit of variable costing = Profit of absorption costing |
No change in inventory |
|
Sales > Production |
Profit of variable costing > Profit of absorption costing |
Decrease in inventory |
|
Sales < Production |
Profit of variable costing < Profit of absorption costing |
Increase in inventory |
Or
|
Profit of variable costing = Profit of absorption costing |
No change in inventory |
No opening , no closing stock* |
|
Profit of variable costing > Profit of absorption costing |
Decrease in inventory |
Opening stock > Closing stock |
|
Profit of variable costing < Profit of absorption costing |
Increase in inventory |
Opening stock < Closing stock |
*Sometime opening stock and closing stock may be equal.
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
If production = sales, net income will be same for variable costing and absorption costing. |
|
If there are not opening stock and closing stock, net income of variable costing = absorption costing. |
|
If sales > production, net income of variable costing will be more than absorption costing. |
|
If sales < production, net income of variable costing will be less than absorption costing. |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3D [production = sales]
Rupandehi Biscuits (P) Ltd keeps its accounting under variable costing system. Following data is available on 31st December:
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 10,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[10,000 units @ $20] |
200,000 |
||
|
(A) |
200,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[10,000 units @ $2] |
20,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[10,000 units @ $3] |
30,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[10,000 units @ $1.5] |
15,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production |
65,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[0 units @ $6.5] |
Nil |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[0 units @ $6.5] |
Nil |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
65,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
135,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
[10,000 @ $1] |
(10,000) |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
[10,000 @ $0.50] |
(5,000) |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
120,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
|
+20,000 |
(50,000) |
|
Net Income |
$70,000 |
|||
Additional information:
Normal output is 20,000 units.
Production is 10,000 units and sales are 10,000 units.
Required: (1) Absorption Costing; (1) Reconciliation Statement
[Answer: Absorption costing = $70,000]
SOLUTION:
Fixed cost per unit [FCPU]
= Factory overhead ÷ Normal output
= $20,000 ÷ 20,000 unit
= $1
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 10,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[10,000 units @ $20] |
200,000 |
||
|
(A) |
200,000 |
|||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[10,000 units @ $2] |
20,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[10,000 units @ $3] |
30,000 |
|
|
|
Variable production cost |
[10,000 units @ $1.5] |
15,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[10,000 units @ $1] |
10,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $7.5) |
75,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[0 units @ $7.5] |
Nil |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[0 units @ $7.5] |
Nil |
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
75,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Under absorption |
[$20,000 in V.C. – $10,000 A.C.] |
10,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Over absorption |
|
– |
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
85,000 |
||
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
115,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
Variable S&D cost |
|
5,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed administrative cost |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
|
10,000 |
(45,000) |
|
Net Income |
70,000 |
|||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable cost |
70,000 |
|
Add: Closing stock (0 units @ $1) |
|
|
Less: Opening stock (0 units @ $1) |
|
|
Net income as per absorption cost |
70,000 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3E [production < sales]
Duggar Snacks (P) Ltd manufactures brand Kurmure in three sizes: big, medium and small. It keeps its accounting in variable costing. The following information is related to medium size on 31st December:
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 45,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[50,000 units @ $20] |
10,00,000 |
||
|
(A) |
10,00,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[45,000 units @ $3] |
135,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[45,000 units @ $2] |
90,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[45,000 units @ $1] |
45,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production |
270,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[15,000 units @ $6] |
90,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[10,000 units @ $6] |
(60,000) |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
300,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
700,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
[45,000 @ $0] |
Nil |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
[50,000 @ $1] |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
650,000 |
||
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
|
150,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution |
|
200,000 |
(400,000) |
|
Net Income |
250,000 |
|||
Additional information:
· Normal output is 50,000 units.
· Production is 45,000 units and sales are 50,000 units.
Required: (a) Absorption costing; (b) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: Absorption costing = $235,000]
SOLUTION:
Fixed cost per unit [FCPU]
= Fixed overhead ÷ Normal output
= $150,000 ÷ 50,000 units
= $3
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 45,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[50,000 units @ $20] |
10,00,000 |
||
|
(A) |
10,00,000 |
|||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
– |
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[45,000 units @ $3] |
1,35,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[45,000 units @ $3] |
90,000 |
|
|
|
Variable production cost |
[45,000 units @ $1] |
45,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[45,000 units @ $3] |
1,35,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $9) |
4,05,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[15,000 units @ $9] |
1,35,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[10,000 units @ $9] |
(90,000) |
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
4,50,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Under absorption |
[150,000 in VC – 135,000 AC] |
15,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Over absorption |
|
– |
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
4,65,000 |
||
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
5,35,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
Nil |
|
|
|
Variable S&D cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed administrative cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
|
200,000 |
(300,000) |
|
Net Income |
235,000 |
|||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per Variable Cost |
250,000 |
|
Add: Closing stock (10,000 units @ $3) |
30,000 |
|
Less: Opening stock (15,000 units @ $3) |
(45,000) |
|
Net income as per Absorption Cost |
235,000 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3F [production > sales]
Cello Writing Instrument (P) Ltd manufactures different kinds of ball pens. The following information is obtained for particular ball pen on 31st December:
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 50,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[45,000 units @ $20] |
900,000 |
||
|
(A) |
900,000 |
|||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[50,000 units @ $3] |
150,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[50,000 units @ $2] |
100,000 |
|
|
|
Variable production cost |
[50,000 units @ $1] |
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[50,000 units @ $3] |
150,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $9 |
450,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[15,000 units @ $9] |
135,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[10,000 units @ $9] |
(90,000) |
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
495,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Under absorption |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
510,000 |
||
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
390,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
Variable S & D cost |
[45,000 units @ $1] |
45,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed administrative cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
|
100,000 |
(225,000) |
|
Net Income |
$165,000 |
|||
Required: (1) Variable costing; (2) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: (1) $180,000; (2) $Different of stock value (45,000 – 30,000) = $15,000;
Hints: Fixed manufacturing cost = $165,000]
SOLUTION:
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 50,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[45,000 units @ $20] |
900,000 |
||
|
(A) |
900,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[50,000 units @ $3] |
150,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[50,000 units @ $2] |
100,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[50,000 units @ $1] |
50,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production @ $6) |
300,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[15,000 units @ $6] |
90,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[10,000 units @ $6] |
(60,000) |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
330,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
570,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
[given] |
(30,000) |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
[45,000 @ $1] |
(45,000) |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
495,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[$150,000 AC + $15,000 under absorbed] |
165,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
[given] |
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
[given] |
100,000 |
(315,000) |
|
Net Income |
180,000 |
|||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
165,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock (15,000 units @ $3) |
45,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock (10,000 units @ $3) |
(30,000) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
180,000 |
Fixed manufacturing cost per unit given in the question $3
Click on the photo for FREE eBooks
#####
Problems and Answers of Absorption and Variable Costing |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3A
Max Company uses direct costing for internal control purchase and absorption costing for external reporting purpose. The following differences are located while comparing the two statements.
|
Items |
Variable Costing |
Absorption Costing |
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
$60,000 |
$60,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost charged |
$25,000 |
$30,000 |
|
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
$40,000 |
$40,000 |
|
|
Variable selling cost per unit |
$2 |
$2 |
|
|
Selling price per unit |
$30 |
$30 |
|
Management also projected the following data for the inventory:
|
Beginning inventory units 1,000 |
Sales units 5,000 |
|
Production units 6,000 |
Closing stock units 2,000 |
Cost of beginning inventory is the same as the cost of production in the period.
Required: Income statement by using absorption costing and variable costing approach
[Answers: Net profit = $30,000; $25,000]
*Over absorption $5,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 3B
XYZ Ltd uses direct costing for internal control purposes and absorption costing for external reporting purposes. The company uses the following unit costs for the one product it manufactures:
Projected cost per unit:
Direct materials $60
Direct labour $38
Variable manufacturing $12
Fixed manufacturing cost $10 (Based on 10,000 units per month)
Variable selling and administrative cost $8
Fixed selling and administrative cost $5.60 (Based on 10,000 units per month)
The projected selling price is $160 per unit.
The fixed costs remain fixed within the relevant range of 4,000 to 16,000 units of production.
Management has also projected the following data for the month:
Opening stock 2,000 units
Production 9,000 units
Sales 7,500 units
Required: projected income statement under direct costing and absorption costing.
[Answer: Variable costing: $1,59,000, Absorption costing: $1,74,000;
* Under absorption cost =100,000 – 90,000 = 10,000]
EP Online Study
Thank you for investing your time.
Please comment on the article.
You can help us by sharing this post on your social media platform.
Jay Google, Jay YouTube, Jay Social Media
जय गूगल. जय युट्युब, जय सोशल मीडिया
The post Absorption costing | Variable costing | Reconciliation Statement | Problems and solutions appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>The post Variable Costing | Absorption vs Variable | Problems and Solutions appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>
Variable Costing | Internal Costing | Direct Costing
Variable costing is also known as internal costing, direct costing and marginal costing.
Variable cost helps to administrator to solve the problem about production planning.
Under this method, production cost is calculated on variable basis.
Variable costing includes direct materials, direct labour and variable manufacturing cost in product cost.
It includes fixed manufacturing cost, administrative, selling and distribution cost in period cost.
Direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost:
= Production units x Cost per unit
Period costing under variable costing = Fixed manufacturing cost + Administrative cost + S&D cost
Total variable, selling and distribution cost = Sales units x Cost per unit
Sold units = Opening stock + Production – Closing stock

Variable costing | Cost allocation
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
There are three types of question: |
|
If question is given, you can be asked to calculate variable costing as well as absorption costing and reconciliation statement. |
|
If variable costing is given in question, you are asked to calculate absorption costing and reconciliation statement. |
|
If absorption costing is given in question, you are asked to calculate variable costing and reconciliation statement. |
Income Statement under Variable Costing
|
Particulars |
Amount $ |
|||
|
Sales revenue (sales units @ $) |
xxxx |
|||
|
(A) |
xxxx |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|||
|
|
Direct materials |
(production units @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
(production units @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Variable production overhead |
(production units @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Total variable cost or Cost of production |
xxxx |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
(opening stock @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
(closing stock @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
(production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
(sales units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Net contribution |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
( ± absorption, if any) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
(production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
(sales units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Net Income |
xxxx |
|||
Note: If there is under absorption in absorption costing, it is added with fixed manufacturing cost in variable costing
If there is over absorption in absorption costing, it is deducted from fixed manufacturing cost in variable costing
Advantage of Variable Costing
The main advantage of variable costing are:
It is simple to understand and easy to apply.
It is useful to managerial decision for profit planning, decision making, and control.
It does not effect to calculate predetermined fixed cost.
It does not have problem relating to over or under absorption manufacturing cost.
It is suitable for standard costing and budgeting.
Breakeven point or cost volume profit analysis is totally depended on variable costing.
Disadvantage or Limitation of Variable Costing
The main disadvantage of variable costing are:
Inventory is valuation variable cost in variable costing.
That is not accepted by tax authority department.
Variable costing insists on selling function.
Manufacturing is also important function.
Variable costing impose/force for variable cost.
But segregation of variable cost from semi variable cost is not easy.
It is suitable only for short term run.
Difference between Absorption Costing and Variable Costing
|
Bases |
Absorption Costing |
Variable Costing |
|
Cost |
Fixed manufacturing overhead is considered as product cost. |
Fixed manufacturing overhead is considered as period cost. |
|
Inventory |
Inventory includes the fixed manufacturing overhead. Therefore, the value of inventory will be higher |
Inventory does not include fixed manufacturing overhead because it is considered as period cost. Therefore the value of inventory will be lower. |
|
Profit |
Higher the units of ending inventory, higher the profit |
Lower the unit of ending inventory, lower will be the profit. |
|
Reporting |
It is suitable for external reporting purpose. |
It is suitable for internal reporting purpose |
|
Over or under absorption |
Under this costing, there may be over or under absorption of fixed manufacturing. |
Under this costing, there will not be over or under absorption of fixed manufacturing. |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2A
ABC Manufactures Company produces a single product; the operating data for February 2020 is given below:
Sales units 1,000 units
Production units 1,000 units
Selling price per unit $500
|
Materials cost per unit: |
Fixed cost: |
||
|
Direct materials |
$60 |
Factory overheads |
$60,000 |
|
Direct labor |
$100 |
Administrative cost |
$80,000 |
|
Variable factory overheads |
$40 |
Selling and distribution cost |
$50,000 |
|
Variable administrative overhead |
$20 |
|
|
|
Variable selling and distribution |
$15 |
|
|
Required: Income statement under variable costing
[Answer: Net income = $60,000]
SOLUTION:
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 1,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount $ |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[1,000 @ $500] |
500,000 |
||
|
|
(A) |
500,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[1,000 @ $60] |
60,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[1,000 @ $100] |
100,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[1,000 @ $40] |
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
Cost of Production [$200,000 ÷ 1,000 units = $200] |
200,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[Units @ $200] |
Nil |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[Units @ $200] |
Nil |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
200,000 |
|
|
|
|
Gross Contribution (A – B) |
300,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
[1,000 @ $20] |
(20,000) |
|
|
Less: |
Variable selling and distribution cost |
[1,000 @ $2] |
(30,000) |
|
|
|
|
Net Contribution |
250,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
|
80,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
|
50,000 |
190,000 |
|
Net Income |
60,000 |
|||
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2B
Following are data pertaining to month of December of operation for BR Textile Company related to school dress textile:
Units sold 5,000 miters
Selling price per unit $200
Units produced 6,000 miters
Fixed manufacturing cost $100,000
Other information:
|
Variable cost: |
Administrative expenses: |
Selling and distribution expenses: |
|
Direct materials $40 |
Fixed $50,000 |
Fixed $30,000 |
|
Direct labor $30 |
Variable $100,000 |
Variable (per unit) $10 |
|
Factory overheads $20 |
|
|
Required: Income statement under variable costing
[Answer: Net income = $220,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold unit |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
5,000 |
= |
Nil + 6,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
1,000 |
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 6,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount $ |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[5,000 @ $200] |
10,00,000 |
||
|
|
(A) |
10,00,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[6,000 @ $40] |
240,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[6,000 @ $30] |
180,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[6,000 @ $20] |
120,000 |
|
|
|
|
Cost of Production @ $90] |
540,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Opening stock |
[0 @ $90] |
Nil |
|
|
Less: |
Closing stock |
[1,000 @ $90] |
(90,000) |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
450,000 |
|
|
|
|
Gross Contribution (A – B) |
550,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
(100,000) |
|
|
Less: |
Variable selling and distribution cost |
[5,000 @ $10] |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
|
Net Contribution |
400,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
|
100,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
|
30,000 |
(180,000) |
|
Net Income |
$220,000 |
|||
Reconciliation of Difference in Net Cost
If there is no difference in the size of opening stock and closing stock, in such a condition net income of absorption costing and variance costing is same.
The difference between opening stock, closing stock and fixed manufacturing overhead are the main cause of difference in net income.
These differences can be solved by reconciliation.
Where:
|
Difference in stock units |
= Difference in income ÷ Fixed cost per unit |
|
According to variable costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units − Difference in stock units |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units + Difference in stock units |
|
|
|
|
According to variable costing, Closing stock– Opening stock |
= Difference |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock – Closing stock |
= Difference |
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Different in income |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Opening stock in units |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Closing stock in units |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Different stock in units (A) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Fixed cost per unit (B) |
x |
x |
|
Different in income (A x B) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
FMC = fixed manufacturing cost per unit |
|
|
FCPU = fixed cost per unit |
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output |
|
SFOR = standard fixed overhead rate |
|
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2C
The extracted data are taken from EP Manufacturing Company:
|
Net profit as per variable costing |
$450,000 |
Fixed cost |
$300,000 |
|
Opening stock |
10,000 units |
Normal output |
40,000 units |
|
Closing stock |
7,000 units |
|
|
Required: Net profit as per absorption costing
[Answer: $427,500]
SOLUTION:
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
= $300,000 ÷ 40,000 units
= $7.50
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable cost |
450,000 |
|
Add: Closing stock (7,000 units @ $7.50) |
52,500 |
|
Less: Opening stock (10,000 units @ $7.50) |
(75,000) |
|
Net income as per Absorption Cost |
427,500 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2D
An absorption costing statement showed a less profit (loss) $8,000 than variable costing with the closing stock was 2,000 units in first year. An excess profit of $16,000 with 4,000 closing stock units in second year. Fixed cost per unit $8 and variable cost per unit $12 were used for two years.
Required: Reconciliation statement for net profit under variable costing system
[Answer: $45,000; ($90,000)]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
|
Difference in profit |
= |
Difference in stock x FCPU |
|
–8,000 |
= |
Difference in stock x $8 |
|
Difference in stock |
= |
–1,000 |
Closing stock
|
Closing stock – Opening stock |
= |
Difference |
|
Closing stock – 5,000 |
= |
– 1,000 |
|
Closing stock |
= |
3,000 units |
Closing stock of first becomes opening stock of second year
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
|
|
|
|
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
|
Net profit as per absorption costing |
|
|
|
|
(8,000) |
16,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock |
3,000 |
2,000 |
@ $8 |
|
24,000 |
16,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock |
2,000 |
4,000 |
@ $8 |
|
(16,000) |
(32,000) |
|
Net profit as per variable costing |
|
|
|
|
45,000 |
(90,000) |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2E
While converting the variable income statement of last two years 2020 and 2021:
(a) The income statement reported loss of $16,000 in 2020 with the opening stock of 5,000 units
(b) Profit of $8,000 with the closing stock of 4,000 units in 2021.
(c) Fixed overhead of $8 per unit was used in both years calculation.
Required: (1) Opening stock in units for 2020; (2) Net profit (loss) of absorption costing by reconciliation statement;
(3) Closing stock in units for 2021
[Answer: (1) Opening stock = 3,000 units;
(2) Year 2020 loss = ($32,000); year 2021 profit = $16,000;
(3) Closing stock in 2021 = 3,000 units]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
|
Difference in profit |
= |
Difference in stock x FCPU |
|
–16,000 |
= |
Difference in stock x $8 |
|
Difference in stock |
= |
–2,000 |
Closing stock
|
Closing stock – Opening stock |
= |
Difference |
|
Closing stock – 5,000 |
= |
– 2,000 |
|
Closing stock |
= |
3,000 units |
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
|
|
|
|
Year 2020 |
Year 2021 |
|
Net profit as per absorption costing |
|
|
|
|
(16,000) |
8,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock |
3,000 |
4,000 |
@ $8 |
|
24,000 |
32,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock |
5,000 |
3,000 |
@ $8 |
|
(40,000) |
(24,000) |
|
Net profit as per variable costing |
|
|
|
|
(32,000) |
16,000 |
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
More or higher profit means net profit |
|
Less or lesser profit means net loss |
|
Use always fixed cost per unit (never use variable cost per unit) |
Click on the photo for FREE eBooks
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2060 Modified
The income statement of XYZ Company based on Absorption costing is given below:
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Amount |
||
|
Sales revenue |
@ $40 each |
|
400,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Manufacturing cost |
|
|
|
|
|
Direct material |
@ $5 each |
45,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
@ $10 each |
90,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing |
@ $10 each |
90,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,25,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Opening stock |
2,000 units @ $25 each |
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,75,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Closing stock |
1000 units @ $25 each |
25,000 |
(2,50,000) |
|
|
|
Gross profit before adjustment |
|
1,50,000 |
|
Less: |
Under absorption of fixed manufacturing cost |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
Gross profit after adjustment |
|
1,40,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Non-manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed cost |
60,000 |
|
|
|
|
Variable cost @ $4 |
40,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
|
Net Income |
|
40,000 |
||
Required: (1) Income statement by using variable costing; (2) Reconciliation of difference in profit
[Answers: (1) $50,000; (2) $10,000] *FMC in V.C = 100,000]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
Sold units = Opening stock + Production – Closing stock
10,000 = 2,000 + 9,000 – 1,000
In the question, there is under absorption manufacturing cost $10,000
Fixed production cost $10,000 units @ $10 per unit.
So, total fxed production cost = $10,000 + $90,000 = $100,000
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 9,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
(10,000 units @ $40) |
4,00,000 |
||
|
|
(A) |
4,00,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
(9,000 units @ $5) |
45,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
(9,000 units @ $10) |
90,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
|
Nil |
|
|
|
|
Cost of production ($1,35,000 ÷ 9,000 units = $15) |
1,35,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
(2,000 @ $15) |
30,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
(1,000 @ $15) |
(15,000) |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
1,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
2,50,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
– |
|
|
Less: |
Variable non-manufacturing |
(10,000 units @ $4) |
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
Net contribution |
2,10,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
[$90,000 A.C + $10,000 under] |
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed non-manufacturing cost |
|
60,000 |
(1,60,000) |
|
Net Income |
$50,000 |
|||
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2061/S Modified
The absorption Costing income Statement of AL Manufacturing Company has been provided as:
Production 22,000 units
Sales unit 25,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
||
|
Sales revenue |
@ $20 (A) |
500,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Cost of goods sold: |
|
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
@ $10 |
220,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing overhead cost |
@ $4 |
88,000 |
|
|
|
Total cost of products @ $14 |
308,000 |
|
Add: |
Value of beginning inventory |
5000 units @ $14 |
70,000 |
|
Less: |
Value of ending inventory |
2000 units @ $14 |
(28,000) |
|
|
|
Total cost of goods sold (B) |
350,000 |
|
|
|
Gross margin before adjustment (A – B) |
150,000 |
|
Add: |
Manufacturing overhead over absorbed |
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
Gross margin after adjustment |
158,000 |
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost @ $3 |
75,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
50,000 |
(125,000) |
|
Net income before tax |
33,000 |
||
Required: (1) Income statement under variable costing; (2) Reconciliation statement
[Answers: (1) $45,000; (2) = $33,000;
*FMC in V.C (88,000 – 8,000) = $80,000]
SOLUTION
Sold units = Opening stock + Production – Closing stock
25,000 = 5,000 + 22,000 – 2,000
Fixed cost per unit = $4* given
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 22,000 units
|
Particulars |
|
Amount |
||
|
Sales revenue |
(25,000 @ $20 |
5,00,000 |
||
|
|
(A) |
5,00,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
|
|
|
|
|
Direct labour |
|
|
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
(22,000 @ $10) |
2,20,000 |
|
|
|
|
Cost of production ($2,20,000 ÷ 22,000 units = $10) |
2,20,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
(5,000 @ $10) |
50,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
(2,000 @ $10) |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
2,50,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
|
– |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
(25,000 @ $3) |
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
Net contribution |
1,75,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
($88,000 – $8,000) |
80,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
|
Nil |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
|
50,000 |
(130,000) |
|
Net Income |
$45,000 |
|||
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2063 Modified
A mill has provided the cost for the annual normal capacity output of 50,000 kg.
|
Direct material cost per kg |
$10 |
|
Direct labour cost per kg |
$8 |
|
Manufacturing overhead per kg |
$10 (50% fixed) |
|
Selling and distribution overhead per kg |
$4 (25% variable) |
|
The selling price per kg |
$35 |
|
The annual fixed administrative expenses incurred |
$100,000 |
|
The mill sold 50,000 kg in the last year. |
|
|
The store ledger recorded 10,000 kg of beginning inventory and 15,000 kg of ending inventory in the period. |
|
Required: Income statement based on variable costing
[Answer: $50,000]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
|
Sold unit |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
50,000 |
= |
10,000 + Production – 15,000 |
|
Production |
= |
55,000 units |
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 55,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
(50,000 units @ $35) |
17,50,000 |
||
|
|
(A) |
17,50,000 |
||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
(55,000 @ $10) |
5,50,000 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
(55,000 @ $8) |
4,40,000 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
(55,000 @ $10@50%) |
2,75,000 |
|
|
|
|
Cost of production ($12,65,000 ÷ 55,000 units = $23) |
12,65,000 |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
(10,000 @ $23) |
2,30,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
(15,000 @ $23) |
(3,45,000) |
|
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
11,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
6,00,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost |
(50,000 @ $4@25%) |
(50,000) |
|
|
Less: |
Variable S&D cost |
|
Nil |
|
|
|
|
Net contribution |
5,50,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed production cost |
(50,000@ $10@50%) |
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
(given) |
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
(50,000 @ $4@75%) |
1,50,000 |
(5,00,000) |
|
Net income |
$50,000 |
|||
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2066 Modified
A Manufacturing Company has reported its income statement under absorption costing technique as under:
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue |
(10,000 units x $45) |
|
450,000 |
|
Less: Cost of goods sold: |
|
|
|
|
Beginning inventory |
(2,000 x $27) |
54,000 |
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
(9,000 x $23) |
207,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
(9,000 x $4) |
36,000 |
|
|
Ending inventory |
(1,000 x $27) |
(27,000) |
(270,000) |
|
Gross margin before adjustment |
|
|
180,000 |
|
Less: Fixed manufacturing cost under absorbed |
|
(4,000) |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost |
|
(50,000) |
|
|
Net income |
|
126,000 |
|
Required: (a) Income statement under variable costing; (b) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: $130,000]
SOLUTION
Income Statement under Variable Costing
For 9,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Sales revenue |
[10,000 units @ $45] |
450,000 |
||
|
(A) |
450,000 |
|||
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
||
|
|
Direct materials |
[9,000 units @ $0] |
Nil |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
[9,000 units @ $0] |
Nil |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
[9,000 units @ $23] |
207,000 |
|
|
|
Cost of production ($207,000 ÷ 9,000 = $23) |
207,000 |
||
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory |
[2,000 units @ $23] |
46,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory |
[1,000 units @ $23] |
(23,000) |
|
|
|
COGS (B) |
230,000 |
||
|
|
Gross contribution (A – B) |
220,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Variable administrative |
|
(50,000) |
|
|
|
Variable S&D |
|
Nil |
|
|
|
Net contribution |
170,000 |
||
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
[$36,000 A.C. + $4,000 under absorbed] |
40,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed administrative cost |
|
Nil |
|
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
|
Nil |
(40,000) |
|
Net income |
$130,000 |
|||
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
126,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock (2,000 units @ $4*) |
8,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock (1,000 units @ $4*) |
(4,000) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
$130,000 |
#####
Problems and Answers of Variable Costing |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2A
Following are data pertaining to month of December of operation for ABC Textile related to school dress:
|
Opening stock 2,000 units |
Administrative expenses: |
|
Units produced 6,000 units |
Fixed $250,000 |
|
Normal output 5,000 units |
Variable $250,000 |
|
Units sold 7,000 units |
Selling and distribution expenses: |
|
Selling price per unit $300 |
Variable (per unit) $20 |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost $200,000 |
Fixed (per unit) $15 |
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
Direct materials $50 |
|
|
Direct labor $40 |
|
|
Factory overheads $30 |
|
Required: (a) Income statement under variable costing; (b) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: (1) Net income = $315,000; (2) $275,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2B
AK Manufacturing Company has reported its income statement under absorption costing technique as under:
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Amount |
||
|
Sales revenue |
(10,000 units x $45) |
|
450,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Cost of goods sold: |
|
|
|
|
|
Beginning inventory |
(2,000 x $27) |
54,000 |
|
|
|
Variable cost |
(9,000 x $23) |
207,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
(9,000 x $4) |
36,000 |
|
|
|
Ending inventory |
(1,000 x $27) |
(27,000) |
(270,000) |
|
|
Gross margin before adjustment |
|
180,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed manufacturing cost under absorbed |
|
(4,000) |
|
|
|
Gross margin after adjustment |
|
176,000 |
|
|
Less: |
Other variable cost |
|
(50,000) |
|
|
Net income before tax |
|
$126,000 |
||
Required: Income statement under variable costing technique
[Answer: Net income under variable costing = $130,000;
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2C
Following details are given to you:
Normal capacity 200,000 units per year
Standard variable manufacturing expenses $20 per unit
Fixed manufacturing overhead $300,000 per year
Variable selling expenses $2 per unit
Fixed selling expenses $100,000
Unit sale price $25
The operating results for the year ending December of the last year were as follows
Sales 150,000 units
Production 180,000 units
Required: (a) variable costing income statement; (b) Reconciled profit under absorption costing
[Answers: Income under VC = $50,000, under AC = $95,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 2D
XYZ Manufacturing Company with normal capacity of 50,000 units supplied you with the following particular:
|
Production |
55,000 units |
|
Sales |
60,000 units |
|
Closing stock |
5,000 units |
|
Unit variable manufacturing cost |
$6 |
|
Unit fixed manufacturing overhead |
$3 |
|
Unit variable selling and administrative cost |
$2 |
|
Fixed selling and administrative cost |
$90,000 |
|
Unit selling price |
$15 |
Required: (1) Variable costing income statement; (2) Reconciled profit under absorption costing
[Answers: (1) $180,000; (2) $165,000]
EP Online Study
Thank you for investing your time.
Please comment on the article.
You can help us by sharing this post on your social media platform.
Jay Google, Jay YouTube, Jay Social Media
जय गूगल. जय युट्युब, जय सोशल मीडिया
The post Variable Costing | Absorption vs Variable | Problems and Solutions appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>The post Absorption Costing | Product Cost | Period Cost | Problems and Solutions appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>
Absorption Costing | External Costing | Traditional Costing
Absorption costing is a traditional costing system.
It is also called full absorption, conventional costing or traditional costing and external costing.
It includes variable cost and fixed cost manufacturing.
Absorption costing includes direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost and fixed manufacturing cost in product cost.
It includes administrative cost, selling and distribution cost in period cost.
But it does not include fixed manufacturing cost in period cost.
The main object of the business company is to earn more and more profit.
Success or failure of the company is depended on profit.
The income statement measures profit or loss of the company.
There are two types of methods to find out profit and loss from income statement.
Absorption costing and variable costing are two methods to prepare income statement.
Absorption costing is suitable for internal as well as external users but variable costing is suitable for internal users with management decision.
Definition of absorption costing
According to ICMA London, “The practice of charging all costs, both variable cost and fixed cost to operation, process or products is called absorption costing.”
Direct materials, direct labour, variable manufacturing cost and fixed manufacturing cost = Production units x Cost per unit
Period cost under absorption costing = Administrative cost + Selling and distribution cost
Total variable, selling and distribution cost = Sales units x Cost per unit

Advantages of Absorption Costing
The main advantages of absorption costing are following:
It has been accepted by FASB, ASC, ASB, taxation department etc for external reporting purpose and inventory valuation.
It makes clear distinguish between manufacturing and non-manufacturing cost.
It provides clear information about efficient or inefficient utilization of capacity by over or under absorption of manufacturing cost.
Under this, work in progress is valued at work cost and finished goods are valued at total cost.
It is useful for price fixation.
It helps to calculate gross profit and net profit separately in income statement.
It helps to management to allocation production and non-production cost etc.
Limitation or Disadvantage of Absorption Costing
The main limitations of absorption costing are following:
It is not suitable for internal purpose viz it is not suitable for managerial decision making.
In absorption costing, fixed manufacturing cost is added with manufacturing cost or product cost.
It is not proper accounting transaction.
It is not helpful to prepare flexible budget; because it does not separate fixed cost and variable cost.
Fixed cost increases value of inventory.
It is not good because fixed cost should not be included in inventory.
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For ….. units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
||
|
Sales Revenue (sales units @ $) |
xxxx |
||
|
(A) |
xxxx |
||
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
||
|
|
Direct materials (production units @ $) |
|
|
|
|
Direct labour (production units @ $) |
|
|
|
|
Variable production overhead (production units @ $) |
|
|
|
|
Fixed production cost (production units @ $*) |
|
|
|
|
Total manufacturing cost or Cost of production |
xxxx |
|
|
Add: |
Beginning inventory (opening stock @ $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Ending inventory (closing stock @ $) |
(xxx) |
|
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
xxxx |
|
|
Add: |
Under absorption manufacturing cost (compare with actual) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Over absorption manufacturing cost (compare with actual) |
(xxx) |
|
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Variable administrative cost (production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Variable S&D cost (sales units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
Less: |
Fixed administrative cost (production units x $) |
xxxx |
|
|
|
Fixed S & D cost (sales units x $) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Net Income |
xxxx |
||
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU*) = Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
Either over absorption# or under absorption
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
FASB = Financial Accounting Standard Board, USA |
|
ASC = Accounting Standard Committee, UK |
|
ASB = Accounting Standard Board, India |
|
|
|
The value of inventory is always over valued in absorption costing |
|
The value of inventory is always undervalued in variable costing. |
|
If actual output units are more than normal outputs units, there will be over absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead |
|
If actual output units are less than normal outputs, there will be under absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead |
|
If actual output units are equal to normal output, neither under absorption nor over absorption. |
######
|
Click on the link for YouTube videos |
|
|
Accounting Equation |
|
|
Journal Entries in Nepali |
|
|
Journal Entries |
|
|
Journal Entry and Ledger |
|
|
Ledger |
|
|
Subsidiary Book |
|
|
Cashbook |
|
|
Trial Balance and Adjusted Trial Balance |
|
|
Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) |
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
Click on the link for YouTube videos chapter wise |
|
|
Financial Accounting and Analysis (All videos) |
|
|
Accounting Process |
|
|
Accounting for Long Lived Assets |
|
|
Analysis of Financial Statement |
|
######
Product Cost
All the expenses related to manufacturing or production is called product cost.
It is also known inventorial cost.
It is used for valuation of inventory.
Product cost is related to direct material, direct labour, consumable supplies and manufacturing overhead.
Product cost can be recorded as an inventory asset if the product has not yet been sold.
Examples of products costs are:
Direct material
Direct labour
Direct or chargeable expenses
Factory overhead
|
Product costing under variable costing |
Product costing under absorption costing |
|
Direct materials |
Direct materials |
|
Direct labour |
Direct labour |
|
Variable manufacturing costs |
Variable manufacturing costs |
|
Fixed manufacturing costs |
Nil |
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
Product cost appears in the financial statements. |
|
Since it includes the manufacturing overhead that is required by both GAAP and IFRS. |
Period Cost
A period cost is also called period expenses.
All the expenses related to administrative, selling and distribution are called period cost.
These costs may be variable or fixed.
Period cost is charged to expense always.
It is not capitalized expenses.
It is not included within the cost of goods sold on the income statement.
But it is included within the administrative and selling expenses.
These costs are NOT part of production or manufacturing or cost of goods sold on income statement.
Generally, period costs are recorded on income statement NOT on balance sheet.
Examples of period costs
General and administrative expenses
Executive and administrative salaries and benefits
Office rent
Depreciation on office equipment
Amortization of intangible assets
Interest expense
Selling expenses
Advertising expenses
Travel and entertainment expenses
Commissions to sales person
Depreciation on warehouse and delivery van etc
Items that are NOT period costs
Direct materials
Direct labour
Direct expenses
Prepaid expenses like insurance and rent
Capitalized expenses (purchase and installation of fixed asset)
|
Period costing under variable costing |
Period costing under absorption costing |
|
Nil |
Fixed manufacturing costs |
|
Administrative cost |
Administrative cost |
|
Selling and distribution cost |
Selling and distribution costs |
Differences between Product Cost and Period Cost
|
Bases |
Product cost |
Period cost |
|
Meaning |
Product cost is related to manifesting of a product. |
Period cost is related to administrative and selling expenses. |
|
Recording |
It is recorded on GOGS section of income statement and ending inventories on the balance sheet. |
It is recorded on the income statement on administrative and selling and distribution section. |
|
Example |
Direct labour, direct materials and manufacturing expenses. |
Administrative and selling and distribution expenses. |
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
These are not period cost: |
|
|
Costs included in prepaid expenses, such as prepaid rent |
|
|
Costs included in inventory, such as direct labor, direct materials, and manufacturing overhead |
|
|
Costs included in fixed assets, such as purchased assets and capitalized interest |
|
|
|
|
|
Under absorption costing |
Under variable costing |
|
Product costs: |
Product costs: |
|
Direct materials |
Direct materials |
|
Direct labour |
Direct labour |
|
Variable manufacturing costs |
Variable manufacturing costs |
|
Fixed manufacturing costs |
Nil |
|
|
|
|
Period cost: |
Period cost: |
|
Nil |
Fixed manufacturing costs |
|
Administrative costs |
Administrative costs |
|
Selling and distribution costs |
Selling and distribution costs |
Treatment of Opening and Closing Stock
In manufacturing company, all manufactured goods may not be sold out during one accounting period.
In such a condition, closing stock remains for current accounting period.
This closing stock becomes opening stock for next accounting period.
Sold units = Opening stock + Production – Closing stock
There are three conditions for opening stock and closing stock
If sales equal to production, there is neither opening stock nor closing stock.
If sales less than production, there must be closing stock.
If sales more than production, there must be opening stock.
Opening stock, Production, Sales and Closing stock
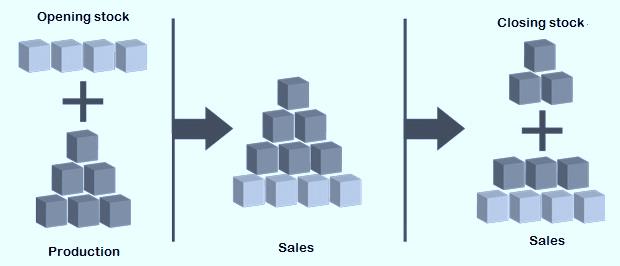
Here,
Opening stock 4,000 units
Production 60,000 unit
Example: 1A
Opening stock 4,000 units
Production 6,000 units
Sales 10,000 units
Explanation:
Here,
Opening stock + production = Sales
So, there is NOT any closing stock
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
10,000 |
= |
4,000 + 6,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= |
10,000 – 10,000 |
|
|
= |
Nil |
Example: 1B
Opening stock 3,000 units
Production 6,000 units
Sales 10,000 units
Here,
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
10,000 |
= |
3,000 + 6,000 – Closing stock |
|
10,000 |
= |
9,000 – Closing stock |
|
– Closing stock |
= |
9,000 – 10,000 |
|
Closing stock |
= |
1,000 units |
Example: 1C
Production 6,000 units
Sales 6,000 units
Explanation:
Here, sales = production, so neither opening stock nor closing stock.
Example: 1D
Production 6,000 units
Sales 7,000 units
Closing stock 3,000 units
Here,
|
Sold units |
= |
Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
7,000 |
= |
Opening stock + 6,000 – 3,000 |
|
7,000 |
= |
Opening stock + 3,000 |
|
7,000 – 3,000 |
= |
Opening stock |
|
Opening stock |
= |
4,000 units |
|
Conditions |
Reason |
Result |
|
Sales = Production |
No change in inventory |
Opening stock = closing stock |
|
Sales > Production |
Decrease in inventory |
Opening stock > closing stock |
|
Sales < Production |
Increase in inventory |
Opening stock < closing stock |
Over or Under Absorption of Manufacturing Cost
While preparing absorption costing income statement, there may be over or under fixed manufacturing cost.
For adjustment of under or over, following points should be kept in mind:
Over absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead
If actual output units are more than normal outputs units, there will be over absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead.
It is also known favorable capacity variances.
It can be either deducted from cost of goods sold or added to the gross margin.
Over absorption
= (Production units – Normal output) x SFOR
= Fixed production cost in AC – Fixed production cost in VC
Where:
FCPU (SFOR) = Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
AC = absorption costing
VC = variable costing
FCPU = fixed cost per unit
SFOR = standard fixed overhead rate
Under absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead
If actual output units are less than normal outputs, there will be under absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead.
It can be either added from cost of goods sold or deducted to the gross margin.
Under absorption
= (Normal output – Production units) x FCPU
= Fixed production cost in VC – Fixed production cost in AC
= Old FMC – New FMC
Where:
FCPU (SFOR) = Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
There are three types of questions: |
|
Question in question |
|
Question in variable costing |
|
Question in absorption costing |
|
|
|
When absorption costing income statement is prepared: |
|
Add: Under absorption [compare with variable costing or question] |
|
Less: Over absorption [compare with variable costing or question] |
|
|
|
When variable costing income statement is prepared: |
|
Under absorption manufacturing cost is added to fixed manufacturing cost |
|
Over absorption manufacturing cost is deducted from fixed manufacturing cost |
|
|
|
Most of the Tribhuvan University questions are given in different ways: |
|
Add: Over absorption [compare with variable costing or question] |
|
Less: Under absorption [compare with variable costing or question] |
|
|
|
Be careful while solving Tribhuvan University questions |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1A
Following are data pertaining to month of December of operation for BR Textile Company related to school dress textile:
|
Units sold 5,000 miters |
Administrative expenses: |
|
Normal output 5,550 miters |
Fixed $50,000 |
|
Selling price per unit $200 |
Variable $100,000 |
|
Units produced 6,000 miters |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost $100,000 |
|
|
|
Selling and distribution expenses: |
|
Variable cost: |
Fixed $30,000 |
|
Direct materials $40 |
Variable (per unit) $10 |
|
Direct labor $30 |
|
|
Factory overheads $20 |
|
Required: Income statement under absorption costing
Answer: Net income = $238,000]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
5,000 |
= Nil + 6,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= 1,000 |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
= $100,000 ÷ 5,550 units
= $18
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 6,000 miters
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue [5,000 @ $200] |
10,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
10,00,000 |
|
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials [6,000 @ $40] |
240,000 |
|
|
Direct labour [6,000 @ $30] |
180,000 |
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost [6,000 @ $20] |
120,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost [6,000 @ $18] |
108,000 |
|
|
Cost of Production @ $108] |
648,000 |
|
|
Add: Beginning inventory (0 @ $108) |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Ending inventory (1,000 @ $108) |
(108,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
540,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Over absorption [$108,000 – $100,000] |
(8,000) |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
532,000 |
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
468000 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost |
100,000 |
|
|
Variable S & D cost [5,000 x $10] |
50,000 |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
50,000 |
|
|
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
+ 30,000 |
(230,000) |
|
Net Income |
238,000 |
|
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1B
Prime Plastic Industries manufactures plastic goods. Following transaction is related to small size item on 31st December:
|
Production |
50,000 units |
Fixed cost: |
|
|
Sales |
40,000 units |
Manufacturing cost |
$200,000 |
|
Closing stock |
15,000 units |
Office expenses |
$50,000 |
|
Normal capacity |
40,000 units |
Selling and distribution expenses |
$1.50 per unit |
|
Selling price per unit |
$20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable cost per unit: |
|
|
|
|
Raw materials |
$5 |
|
|
|
Direct labour |
$3 |
|
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
$2 |
|
|
|
Variable administrative cost |
$1 |
|
|
|
Variable selling and distribution |
$0.50 |
|
|
Required: Income statement under absorption costing
[Answer: $70,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
40,000 |
= Opening stock + 50,000 – 15,000 |
|
Opening stock |
= 5,000 |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
= $200,000 ÷ 40,000 units
= $5
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 50,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue [40,000 @ $20] |
800,000 |
|
|
(A) |
800,000 |
|
|
Variable cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials [50,000 @ $5] |
250,000 |
|
|
Direct labour [50,000 @ $3] |
150,000 |
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost [50,000 @ $2] |
100,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost [50,000 @ $5] |
250,000 |
|
|
Cost of Production @ $15] |
750,000 |
|
|
Add: Opening stock (5,000 @ $15) |
75,000 |
|
|
Less: Closing stock (15,000 @ $15) |
(225,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
600,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption |
– |
|
|
Less: Over absorption [$250,000 – $200,000] |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross profit after adjustment (B) |
550,000 |
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
250,000 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost [50,000 x $1] |
50,000 |
|
|
Variable S&D cost [40,000 x $0.5] |
20,000 |
|
|
Less: Fixed office cost |
50,000 |
|
|
Fixed S&D cost [40,000 x $1.5] |
60,000 |
(180,000) |
|
Net Income |
70,000 |
|
Reconciliation of Difference in Net Cost
If there is no difference in the size of opening stock and closing stock, in such a condition net income of absorption costing and variance costing is same.
The difference between opening stock, closing stock and fixed manufacturing overhead are the main cause of difference in net income.
These differences can be solved by reconciliation.
Where:
|
Difference in stock units |
= Difference in income ÷ Fixed cost per unit |
|
According to variable costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units − Difference in stock units |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock in units |
= Closing stock in units + Difference in stock units |
|
|
|
|
According to variable costing, Closing stock– Opening stock |
= Difference |
|
According to absorption costing, Opening stock – Closing stock |
= Difference |
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) |
xxxx |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) |
(xxx) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
Or
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Different in income |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Opening stock in units |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Closing stock in units |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Different stock in units (A) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
|
Fixed cost per unit (B) |
x |
x |
|
Different in income (A x B) |
xxxx |
xxxx |
Keep in Mind (KIM)
|
FMC = fixed manufacturing cost per unit |
|
|
FCPU = fixed cost per unit |
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output |
|
SFOR = standard fixed overhead rate |
|
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1C
The extracted data are taken from EP Manufacturing Company:
|
Net profit as per absorption costing |
$450,000 |
Fixed cost |
$300,000 |
|
Opening stock |
10,000 units |
Normal output |
40,000 units |
|
Closing stock |
7,000 units |
|
|
Required: Net profit as per variable costing
[Answer: $472,500]
SOLUTION:
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Fixed manufacturing cost ÷ Normal output
= $300,000 ÷ 40,000 units
= $7.50
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
450,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock (10,000 units @ $7.50) |
75,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock (7,000 units @ $7.50) |
(52,500) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
$472,500 |
Click on the photo for FREE eBooks
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2060/S Modified
The income statement of a company under variable costing technique is given below:
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Amount |
|
Sales revenue @ $20 each |
|
360,000 |
|
Less: Variable cost of production @ $12 per unit |
252,000 |
|
|
Add: Opening stock |
12,000 |
|
|
Less: Closing stock |
(48,000) |
216,000 |
|
Contribution margin |
|
144,000 |
|
Less: Non variable or constant cost: |
|
|
|
Fixed factory overhead |
50,000 |
|
|
Fixed selling & administrative expenses |
10,000 |
(60,000) |
|
Net income |
|
84,000 |
Consider normal capacity 20,000 units
Required: (1) Income statement for external reporting; (2) Reconciliation statement showing reasons for difference in profit
[Answer: (1) $91,500; (2) $84,000; * Over absorption = $2,500]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Opening Stock + Production – Closing Stock |
|
18,000 |
= 1,000 + Production – 4,000 |
|
Production |
= 21,000 |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Fixed manufacturing overhead ÷ Normal output
= $50,000 ÷ 20,000 units
= $2.50
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 21,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue (18,000 units @ 20) |
3,60,000 |
|
|
(A) |
3,60,000 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials |
NIL |
|
|
Direct labour |
NIL |
|
|
Variable production overhead (21,000 units @ $12) |
2,52,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost (21,000 units @ $2.50) |
52,500 |
|
|
Cost of production @ $14.5) |
3,04,500 |
|
|
Add: Beginning inventory (1,000 units @ $14.5) |
14,500 |
|
|
Less: Ending inventory (4,000 units @ $14.5) |
(58,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
2,61,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Over absorption ($52,500 in A.C. – $50,000 in V.C.) |
(2,500) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
258,500 |
|
|
Gross profit (A − B) |
1,01,500 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost |
Nil |
|
|
Variable S&D |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
Nil |
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
10,000 |
(10,000) |
|
Net Income |
$91,500 |
|
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net Income as per absorption costing |
91,500 |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) 1,000 units x $2.50 |
2,500 |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) 4,000 units x $2.50 |
(10,000) |
|
Net profit as per variable costing |
$84,000 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2061 Modified
Following information were supplied by AH Manufacturing Concern for the year ended December 31:
|
Normal production capacity 25,000 units |
Non-production fixed expenses $6,250 |
|
Variable production cost per unit $7 |
Variable administrative and selling expenses $0.25 per unit sold |
|
Fixed production cost $62,500 |
Closing stock 2,500 units |
|
Actual production and sales 21,000 units |
Unit selling price $16 |
Required: (1) Income statement necessary for external reporting; (2) Reconcile profit under variable costing
[Answers: (1) $115,000; (2) $115,000]
* Under absorption = $10,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
21,000 |
= Opening stock + 21,000 – 2,500 |
|
Opening stock |
= 2,500 units |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Manufacturing Overhead ÷ Normal Output
= $50,000 ÷ 20,000 units
= $2.50
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 21,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue (21,000 units @ 16) |
3,36,000 |
|
|
(A) |
3,36,000 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials |
Nil |
|
|
Direct labour |
Nil |
|
|
Variable production overhead (21,000 units @ $7) |
1,47,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost (21,000 units @ $2.50) |
52,500 |
|
|
Cost of production @ $9.5) |
1,99,500 |
|
|
Add: Beginning inventory (2,500 units @ $9.5) |
23,750 |
|
|
Less: Ending inventory (2,500 units @ $9.5) |
(23,750) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
1,99,500 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption ($62,500 – $52,500) |
10,000 |
|
|
Less: Over absorption |
Nil |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
209,500 |
|
|
Gross profit (A − B) |
1,26,500 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost |
NIL |
|
|
Variable S & D cost (21,000 units @ $0.25) |
5,250 |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
6,250 |
|
|
Fixed S & D cost |
NIL |
(11,500) |
|
Net Income |
$1,15,000 |
|
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net Income as per Absorption Cost |
1,15,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) 2,500 units x $2.50 |
6,250 |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) 2,500 units x $2.50 |
(6,250) |
|
Net profit as per variable cost |
$1,15,000 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2062 Modified
The data relating to income statement of a company have been provided below:
|
Normal capacity volume |
25,000 units |
Fixed manufacturing cost |
$100,000 |
|
Actual production volume |
28,000 units |
Variable selling and distribution cost |
$2 per unit |
|
Sales unit |
30,000 units |
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
$50,000 |
|
Ending inventory |
3,000 units |
Selling price per unit |
$30 |
|
Variable manufacturing cost per unit |
$20 |
|
|
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answers: (1) $82,000 and (2) $90,000]
*Over absorption = $12,000]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Beginning inventory + Production – Ending inventory |
|
30,000 |
= Beginning inventory + 28,000 – 3,000 |
|
Beginning inventory |
= 5,000 units |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Manufacturing Overhead ÷ Normal Output
= $100,000 ÷ 25,000 units
= $4
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 28,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue (30,000 units @ 30) |
9,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
9,00,000 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials |
Nil |
|
|
Direct labour |
Nil |
|
|
Variable production overhead (28,000 units @ $20) |
5,60,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost (28,000 units @ $4) |
1,12,000 |
|
|
Cost of production @ $24) |
6,72,000 |
|
|
Add: Beginning inventory (5,000 units @ $24) |
1,20,000 |
|
|
Less: Ending inventory (3,000 units @ $24) |
(72,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
7,20,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Over absorption (New $112,000 – Old $100,000) |
(12,000) |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
7,08,000 |
|
|
Gross profit (A − B) |
1,92,000 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost |
NIL |
|
|
Variable S & D cost (30,000 units @ $2) |
60,000 |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
Nil |
|
|
Fixed S & D cost |
50,000 |
(1,10,000) |
|
Net Income |
$82,000 |
|
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net Income as per absorption cost |
82,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock (units @ FCPU) 5,000 units x $4 |
20,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock (units @ FCPU) 3,000 units x $4 |
(12,000) |
|
Net profit as per variable cost |
$90,000 |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2064 Modified
ABC Manufacturing has following extracted data:
The estimated annual fixed costs for the capacity output of 20,000 units are as follows:
|
Factory overhead |
$100,000 |
The estimated variable cost per unit: |
|
|
Office overheads |
$50,000 |
Material cost |
$5 |
|
Selling and distribution overheads |
$75,000 |
Labour |
$3 |
|
|
|
Factory overheads |
$2 |
|
|
|
Selling & distribution overheads |
$2 |
The selling price per unit is fixed $25. The factory has beginning inventory 5,000 units and finalized the production schedule for 25,000 units with a sales forecast 28,000 units.
Required: Budgeted absorption costing income statement.
[Answer: Net income = $124,000; * Over absorption = $25,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
28,000 |
= 5,000 + 25,000 – Closing stock |
|
Closing stock |
= 2,000 units |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= $100,000 ÷ 20,000 units
= $5
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 25,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue (28,000 units @ $25) |
7,00,000 |
|
|
(A) |
7,00,000 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials (25,000 units@ $5) |
1,25,000 |
|
|
Direct labour (25,000 units@ $3) |
75,000 |
|
|
Variable production overhead (25,000 units @ $2) |
50,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost (25,000 units @ $5) |
1,25,000 |
|
|
Cost of production (Rs 3,75,000 ÷ 25,000 units = $15) |
3,75,000 |
|
|
Add: Opening stock (5,000 units @ $15) |
75,000 |
|
|
Less: Closing stock (2,000 units @ $15) |
(30,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
4,20,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Over absorption ($125,000 new – $100,000 old) |
(25,000) |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
395,000 |
|
|
Gross profit (A − B) |
3,05,000 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative |
50,000 |
|
|
Variable S & D cost (28,000 units @ $2) |
56,000 |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
Nil |
|
|
Fixed S & D cost |
75,000 |
(181,000) |
|
Net Income |
$1,24,000 |
|
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2065 Modified
AM Manufactures Company produces a single product. The normal level of operation is 40,000 units. Data for the last financial year were as follows:
|
Production units |
30,000 |
Variable cost per unit: |
|
|
Sales units |
35,000 |
Direct materials |
$5 |
|
Closing stock |
Nil |
Direct labour |
$4 |
|
Fixed manufacturing overhead |
$200,000 |
Other direct expenses (manufacturing) |
$2 |
|
Fixed selling overhead |
$105,000 |
Selling overhead |
4% of selling price |
|
Selling price per unit |
$25 |
|
|
Required: Income statement under absorption costing
[Answer: $125,000] * Under absorption = $50,000]
SOLUTION:
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Opening stock + Production – Closing stock |
|
35,000 |
= Opening stock + 30,000 – Nil |
|
Opening stock |
= 5,000 units |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= $200,000 ÷ 40,000 units
= $5
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 30,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue (35,000 units @ $25) |
875,000 |
|
|
(A) |
875,000 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost: |
|
|
|
Direct materials (30,000 units@ $5) |
150,000 |
|
|
Direct labour (30,000 units@ $4) |
120,000 |
|
|
Variable production overhead (30,000 units @ $2) |
60,000 |
|
|
Fixed production cost (30,000 units @ $5) |
150,000 |
|
|
Cost of production @ $16) |
480,000 |
|
|
Add: Opening stock (5,000 units @ $16) |
80,000 |
|
|
Less: Closing stock (0 units @ $16) |
Nil |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
560,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption ($200,000 old – $150,000 new) |
50,000 |
|
|
Less: Over absorption |
Nil |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
610,000 |
|
|
Gross profit (A − B) |
265,000 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative |
Nil |
|
|
Variable S & D cost (sales @ 4%) |
35,000 |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
Nil |
|
|
Fixed S & D cost |
105,000 |
(140,000) |
|
Net Income |
$125,000 |
|
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
TU: 2067 Modified
The manufacturing overhead of ML Industries for last year was $200,000. The fixed administrative overhead was $150,000 and fixed selling and distribution overhead was $75,000. The variable costs per unit of the industries are as follows:
|
Material cost |
$8 |
Variable manufacturing overhead |
$7 |
|
Direct wages |
$6 |
Variable selling and distribution overhead |
$4 |
The normal capacity output was 40,000 units.
The industries realized 44,000 units of output during the period and it has 5,000 units of beginning finished goods in that period.
The industries sold 45,000 units during the period at $36 per unit.
Required: (1) Income statement based on absorption costing; (2) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: Net profit: Absorption = $65,000; Variable = $70,000]
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
|
Sold units |
= Beginning inventory + Production – Ending inventory |
|
45,000 |
= 5,000 + 44,000 – Ending inventory |
|
Ending inventory |
= 4,000 units |
Fixed cost per unit (FCPU)
= Manufacturing Overhead ÷ Normal Output
= $200,000 ÷ 40,000 units
= $4
Income Statement under Absorption Costing
For 44,000 units
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Sales revenue [45,000 @ $36] |
16,20,000 |
|
|
(A) |
16,20,000 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost: |
. |
|
|
Direct materials [44,000 @ $8] |
352,000 |
|
|
Direct labour [44,000 @ $6] |
264,000 |
|
|
Variable manufacturing cost [44,000 @ $7] |
308,000 |
|
|
Fixed manufacturing cost [44,000 @ $5] |
220,000 |
|
|
Cost of production @ $26] |
11,44,000 |
|
|
Add: Beginning inventory [5,000 @ $26) |
130,000 |
|
|
Less: Ending inventory [4,000 @ $26) |
(104,000) |
|
|
COGS before adjustment |
11,70,000 |
|
|
Add: Under absorption |
Nil |
|
|
Less: Over absorption [$220,000 new – $200,000 old] |
20,000 |
|
|
COGS after adjustment (B) |
11,50,000 |
|
|
Gross profit (A–B) |
470,000 |
|
|
Less: Variable administrative cost |
Nil |
|
|
Variable S&D cost [45,000 x $4] |
180,000 |
|
|
Less: Fixed administrative cost |
150,000 |
|
|
Fixed S&D cost |
75,000 |
(405,000) |
|
Net Income |
$65,000 |
|
Reconciliation Statement
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Net income as per absorption costing |
65,000 |
|
Add: Opening stock (Units x FCPU viz 5,000 @ $5) |
25,000 |
|
Less: Closing stock (Units x FCPU viz 4,000 @ $5) |
(20,000) |
|
Net income as per variable costing |
$70,000 |
#####
Problems and Answers of Absorption Costing |
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1A
The cost abstract of EP Manufacturing Company was as follows:
|
Particulars |
Units cost |
The operations of the year ended December were: |
|
|
Direct materials |
$12 |
Opening stock |
10,000 units |
|
Direct labour |
$3 |
Production |
90,000 units |
|
Variable manufacturing cost |
$2 |
Sales |
80,000 units |
|
Variable selling & distribution expenses |
$1 |
Sales price per unit |
$30 |
Budgeted normal output was 100,000 units with $200,000 fixed manufacturing cost. The fixed selling and distribution expenses were $50,000
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answer: Net profit: A.C = $730,000; V.C = $710,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1B
The summarized data of a manufacturing concern for a capacity output of 50,000 units for a year is reported as:
|
Items |
Units Cost |
Items |
Cost |
|
Direct materials |
$14 |
Fixed manufacturing overhead |
$75,000 annual |
|
Direct labour |
$6 |
Fixed selling expenses |
$50,000 annual |
|
Variable manufacturing overhead |
$4 |
Production |
45,000 units |
|
Variable selling expenses |
$2 |
Sales |
40,000 units |
|
Sales price per unit |
$30 |
|
|
Required: (1) Absorption costing income statement; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answers: (1) Net income = $42,500; (2) $35,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1C
ABC Manufacturing Company with normal capacity of 20,000 units furnished you the following information:
|
Beginning inventory units |
3,000 |
Standard variable cost |
$6.50 |
|
Units produced during the year |
18,000 |
Fixed factory overhead at normal capacity |
$50,000 |
|
Units sold during the year |
20,000 |
Fixed selling and distribution cost |
$5,000 |
|
|
|
Unit selling price |
$12 |
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciled profit under variable costing
[Answers: (1) $50,000; (2) $55,000] *Under absorption = $5,000]
Here, Amount = Rs = $ = £ = € = ₹ = Af = ৳ = Nu = Rf = රු = Br = P = Birr = Currency of your country
PROBLEM: 1D
Following are the references data of month June of operation for XYZ Company:
|
Opening stock |
15,000 units |
Variable cost: |
|
|
Units produced |
45,000 units |
Direct materials per unit |
$4 |
|
Units sold |
50,000 units |
Direct labour per unit |
$2 |
|
Normal output |
50,000 units |
Factory overheads per unit |
$1 |
|
Selling price per unit |
$20 |
Administrative |
$50,000 |
|
Fixed manufacturing cost |
$150,000 |
Selling and distribution per unit |
$1 |
|
|
|
Fixed cost: |
|
|
|
|
Manufacturing |
$150,000 |
|
|
|
Administrative |
$40,000 |
|
|
|
Selling and distribution |
$30,000 |
Required: (1) Income statement under absorption costing; (2) Reconciliation statement
[Answer: (1) Net income = $315,000; (2) $330,000]
EP Online Study
Thank you for investing your time.
Please comment on the article.
You can help us by sharing this post on your social media platform.
Jay Google, Jay YouTube, Jay Social Media
जय गूगल. जय युट्युब, जय सोशल मीडिया
The post Absorption Costing | Product Cost | Period Cost | Problems and Solutions appeared first on EP Online Study.
]]>
